Understanding Graves' Disease
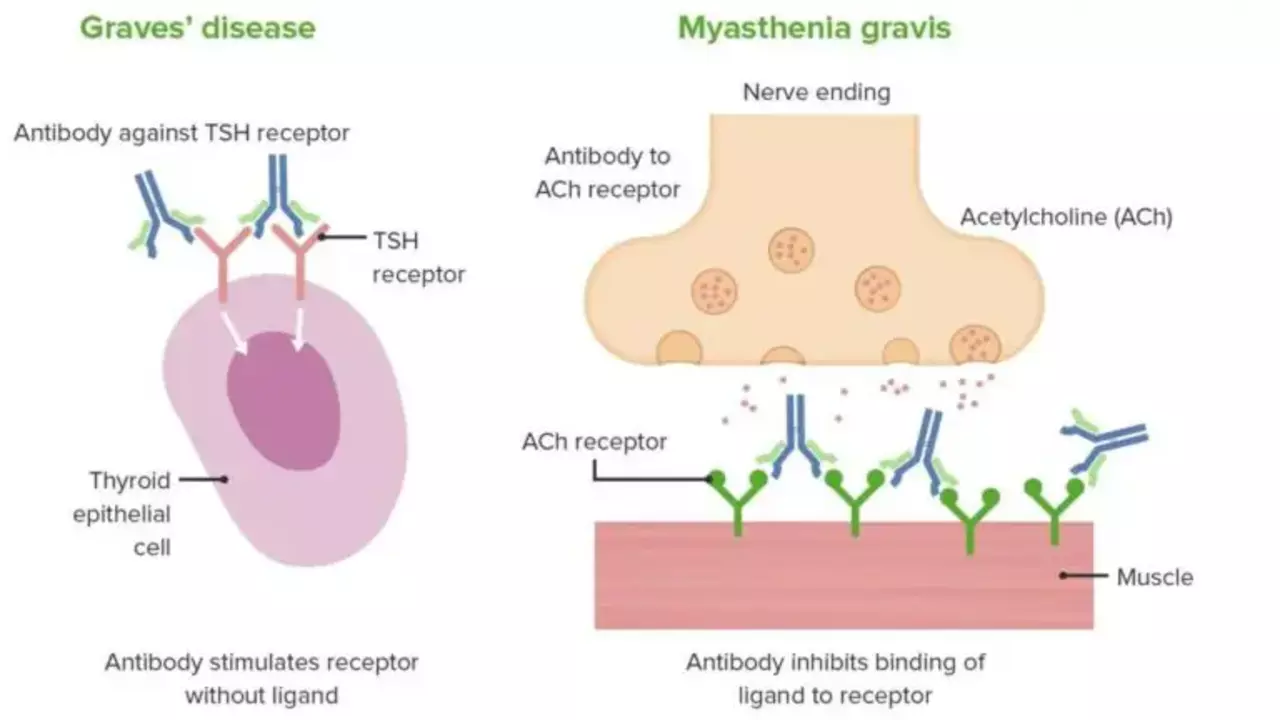
Graves' disease is an autoimmune disorder that results in an overactive thyroid (hyperthyroidism). This means your thyroid gland produces more hormones than your body needs, which can lead to a variety of health issues. Symptoms of Graves' disease can range from weight loss and increased appetite to anxiety, irritability, and rapid heart rate. In severe cases, it can cause thyroid eye disease and skin problems. Graves' disease is more common in women and can occur at any age, but it's most common in women in their 20s and 30s.
The Link Between Graves' Disease and Pregnancy
Graves' disease can affect pregnancy in multiple ways. The thyroid hormones are crucial for the normal development of your baby, and an overactive thyroid can pose several risks. These risks include preterm birth, low birth weight, and preeclampsia. In some cases, it can also lead to a potentially life-threatening condition called thyroid storm. Therefore, it's crucial to manage Graves' disease effectively during pregnancy.
Graves' Disease Symptoms in Pregnancy
During pregnancy, some of the symptoms of Graves' disease may be similar to normal pregnancy symptoms, making it difficult to diagnose. These symptoms include increased heart rate, fatigue, and heat intolerance. However, more severe symptoms such as rapid and irregular heartbeat, severe nausea and vomiting, and weight loss despite a good appetite may indicate Graves' disease. If you experience these symptoms, it's essential to consult your healthcare provider immediately.
The Impact of Graves' Disease on the Baby
The impact of Graves' disease on the baby can be significant. If the disease is not properly managed, it can lead to preterm birth, low birth weight, or even miscarriage. In some cases, untreated Graves' disease can cause thyrotoxicosis (high levels of thyroid hormones) in the baby, which can lead to a rapid heart rate and may affect the baby's growth and brain development.
Managing Graves' Disease During Pregnancy
Managing Graves' disease during pregnancy is crucial to ensure the health of both the mother and the baby. The goal of treatment is to keep thyroid hormone levels within the normal range. This often involves antithyroid medications, beta-blockers, or in some cases, surgery. Regular monitoring of thyroid hormone levels throughout pregnancy is also crucial.
Treatment Options for Graves' Disease in Pregnancy
The treatment options for Graves' disease during pregnancy include antithyroid drugs and beta-blockers. Antithyroid drugs, such as propylthiouracil and methimazole, work by reducing the production of thyroid hormones. Beta-blockers are used to manage symptoms such as rapid heart rate and tremors. In some cases, surgery to remove all or part of the thyroid gland may be recommended. However, surgery is usually considered only if other treatments are ineffective or if there's a large goiter.
Living with Graves' Disease in Pregnancy
Living with Graves' disease during pregnancy can be challenging, but with proper management, it's possible to have a healthy pregnancy. Regular check-ups, following your treatment plan, and taking care of your overall health are crucial. It's also important to monitor your symptoms and report any changes to your healthcare provider immediately. With the right care and support, you can manage Graves' disease and have a healthy pregnancy.
Postpartum and Graves' Disease
After giving birth, women with Graves' disease need to continue their treatment and monitoring. In some cases, thyroid hormone levels may change after pregnancy, requiring adjustments in medication. The postpartum period is also a time of increased risk for Graves' disease flare-ups, so close monitoring is crucial. Breastfeeding is generally safe while taking antithyroid drugs, but it's always best to consult with your healthcare provider.
Final Thoughts
Graves' disease can pose challenges during pregnancy, but with proper care and management, you can have a healthy pregnancy and baby. It's essential to work closely with your healthcare provider, monitor your symptoms, and adhere to your treatment plan. And remember, every pregnancy is unique, so what works for one woman may not work for another. Stay positive, take care of your health, and look forward to welcoming your little one into the world.




Will RD
July 16, 2023 AT 05:42Jacqueline Anwar
July 18, 2023 AT 05:15Ganesh Kamble
July 19, 2023 AT 23:13Jenni Waugh
July 21, 2023 AT 19:24Theresa Ordonda
July 23, 2023 AT 13:30Judy Schumacher
July 23, 2023 AT 18:23Megan Raines
July 24, 2023 AT 21:25Mamadou Seck
July 25, 2023 AT 05:26Anthony Griek
July 27, 2023 AT 00:08Norman Rexford
July 28, 2023 AT 16:20Wayne Keller
July 30, 2023 AT 04:04Shana Labed
July 30, 2023 AT 06:25California Daughter
July 30, 2023 AT 17:13Vishwajeet Gade
July 31, 2023 AT 01:16Casey Crowell
July 31, 2023 AT 10:01Shanna Talley
August 1, 2023 AT 12:55Gina Damiano
August 1, 2023 AT 12:57