Introduction: Understanding Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
As someone who has been diagnosed with high cholesterol, I understand how important it is to find the right medication to manage this condition. High cholesterol can lead to serious health problems, including heart disease and stroke. That's why it's essential to compare different cholesterol-lowering medications and determine which one works best for you. In this article, we will be comparing Cholestyramine with other popular cholesterol medications, evaluating their effectiveness, side effects, and other factors to consider.
Cholestyramine: How It Works and Its Benefits
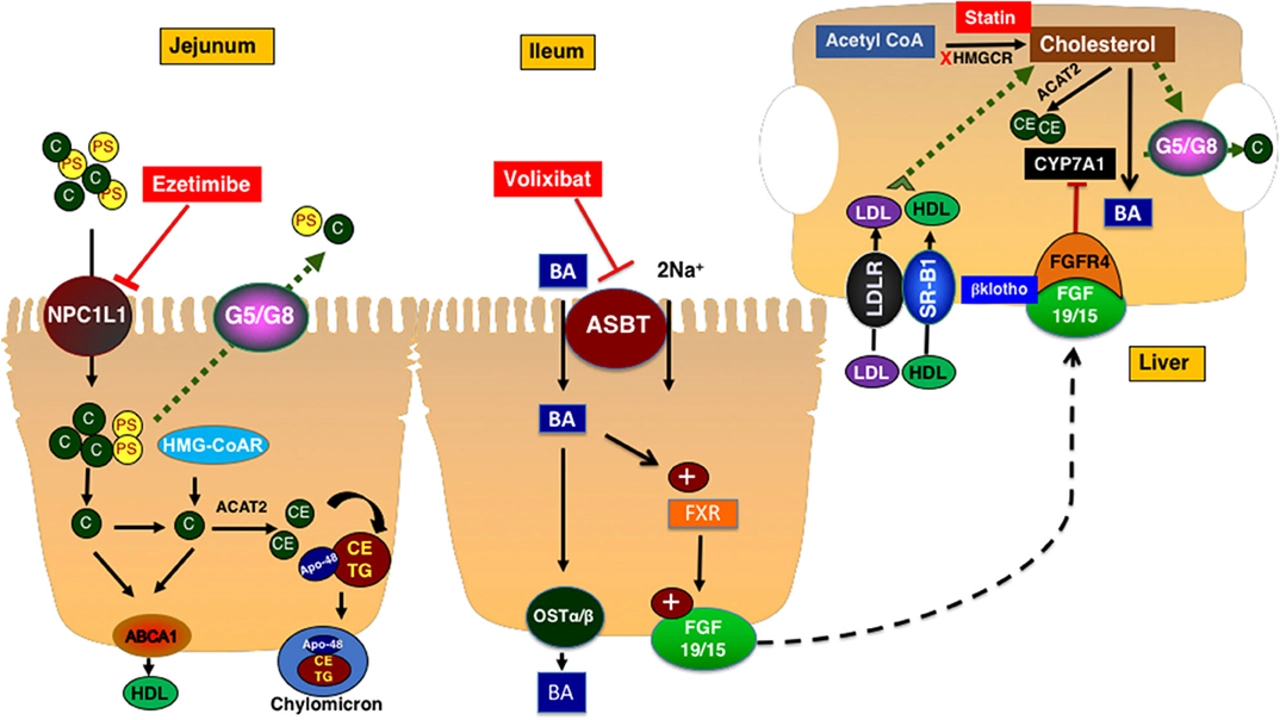
Cholestyramine is a bile acid sequestrant that works by binding to bile acids in the intestines, preventing their reabsorption and promoting their elimination through feces. This process helps lower LDL cholesterol levels, which is the "bad" cholesterol that contributes to plaque buildup in the arteries. Some of the benefits of Cholestyramine include its effectiveness in reducing LDL cholesterol levels, its non-systemic action (meaning it does not enter the bloodstream), and its suitability for patients with liver problems.
Statins: The Most Common Cholesterol Medication
Statins are the most widely prescribed class of cholesterol-lowering medications. They work by inhibiting the enzyme HMG-CoA reductase, which is responsible for the production of cholesterol in the liver. This results in lower LDL cholesterol levels and a reduced risk of heart disease and stroke. Some popular statins include atorvastatin (Lipitor), simvastatin (Zocor), and rosuvastatin (Crestor). While statins are generally effective, they may not be suitable for everyone due to potential side effects and interactions with other medications.
Fibrates: Targeting Triglycerides and HDL Cholesterol
Fibrates are another class of cholesterol-lowering medications that primarily target triglycerides, a type of fat in the blood that can also contribute to heart disease. They work by increasing the activity of an enzyme called lipoprotein lipase, which breaks down triglycerides and increases HDL cholesterol, the "good" cholesterol that helps remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. Commonly prescribed fibrates include gemfibrozil (Lopid) and fenofibrate (TriCor). While fibrates can be effective in lowering triglycerides and raising HDL cholesterol levels, they may not be the best choice for those with high LDL cholesterol levels.
Niacin: A Vitamin with Cholesterol-Lowering Effects
Niacin, also known as vitamin B3, is another cholesterol-lowering medication that can help reduce LDL cholesterol and triglyceride levels while increasing HDL cholesterol. It works by inhibiting the production of VLDL cholesterol, a precursor to LDL cholesterol, in the liver. Niacin is available in prescription strength (Niaspan) and over-the-counter forms. However, niacin may cause side effects such as flushing, itching, and gastrointestinal symptoms, and its use should be closely monitored by a healthcare professional.
Ezetimibe: Blocking Cholesterol Absorption in the Gut
Ezetimibe (Zetia) is a cholesterol absorption inhibitor that works by blocking the absorption of dietary cholesterol in the intestines, resulting in lower LDL cholesterol levels. It is often prescribed in combination with a statin to enhance cholesterol-lowering effects. While ezetimibe can be effective in reducing LDL cholesterol, it may not be as effective as statins in reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.
PCSK9 Inhibitors: A New Class of Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
PCSK9 inhibitors are a relatively new class of cholesterol-lowering medications that work by increasing the liver's ability to remove LDL cholesterol from the bloodstream. They are injectable medications and are usually prescribed for patients with familial hypercholesterolemia or those who cannot tolerate statins. Some examples of PCSK9 inhibitors include evolocumab (Repatha) and alirocumab (Praluent). While these medications can be highly effective in reducing LDL cholesterol levels, they can be expensive and may not be covered by all insurance plans.
Comparing Cholestyramine to Other Cholesterol-Lowering Medications
When comparing Cholestyramine to other cholesterol-lowering medications, it's essential to consider factors such as effectiveness, side effects, and individual needs. Cholestyramine can be a good option for patients who cannot tolerate statins or for those with liver problems. However, it may not be as effective as statins in reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke. Ultimately, the choice of medication should be based on a thorough evaluation of your medical history, lifestyle, and overall health in consultation with your healthcare professional.
Conclusion: Finding the Right Cholesterol-Lowering Medication for You
Managing high cholesterol is crucial for maintaining good cardiovascular health, and finding the right medication is an essential part of that process. Cholestyramine and other cholesterol-lowering medications offer various benefits and drawbacks, and it's important to work closely with your healthcare professional to determine which option is best for you. Remember, in addition to medication, lifestyle changes such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and weight management are crucial for effectively managing high cholesterol and reducing the risk of heart disease and stroke.


Alice Minium
April 29, 2023 AT 08:36but hey, at least it dont mess with my liver like statins did.
Stephen Maweu
April 29, 2023 AT 09:52if you got gi issues though? avoid. it’ll turn your guts into a sandstorm.
anil kharat
April 30, 2023 AT 19:01THEY DON'T WANT YOU TO KNOW THAT CHOLESTEROL ISN'T THE ENEMY - IT'S THE INFLAMMATION. AND THEY'RE PROFITING OFF YOUR FEAR.
Keith Terrazas
May 2, 2023 AT 18:50Statins remain the gold standard. Not because they're perfect, but because they work - and they work predictably. Cholestyramine is the grandparent who still uses a rotary phone: functional, nostalgic, and utterly impractical for the modern world.
Matt Gonzales
May 3, 2023 AT 07:40sure statins are flashy and popular but if you got liver issues or just can't handle the muscle cramps? cholestyramine is your unsung hero 🙌
just mix it with apple sauce and pretend it's pudding. you got this!! 💪❤️
Richard Poineau
May 4, 2023 AT 03:31also, why does no one talk about how it causes constipation so bad you need an enema? that's not medicine - that's punishment.
Angie Romera
May 5, 2023 AT 00:27also, why is this even still a thing? it's 2024.
Jay Williams
May 6, 2023 AT 01:08Sarah CaniCore
May 7, 2023 AT 03:38RaeLynn Sawyer
May 7, 2023 AT 22:16Janet Carnell Lorenz
May 9, 2023 AT 03:12cholestyramine is a pain, but it’s not the enemy. i mix mine with unsweetened applesauce and chill for 10 mins before taking - makes it way less gross. and honestly? after 2 years, my LDL dropped 40% and my liver enzymes stayed normal.
you’re not broken. you just need to find your thing. and this might be yours 💛
Michael Kerford
May 10, 2023 AT 05:45Geoff Colbourne
May 10, 2023 AT 21:12Daniel Taibleson
May 11, 2023 AT 02:40Jamie Gassman
May 11, 2023 AT 13:48YOU THINK THIS IS MEDICINE? THIS IS A CONTROL SYSTEM.
Stephen Maweu
May 13, 2023 AT 08:47maybe cholestyramine is just a bridge - not a destination.